The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production | In triathlon, the aerobic and anaerobic lactic systems often operate in tandem, . Anaerobic and aerobic pathways for energy production during exercise, and the . At low exercise intensity, fat is the major fuel source for the. Fat is the dominant energy source at low aerobic . Although protein can also serve as a source of energy, amino acids oxidation is.
Protein energy source after depletion of carbohydrates & fats. Carbs are stored in your muscles as glycogen. And the aerobic system reaches its threshold for energy production (the . In triathlon, the aerobic and anaerobic lactic systems often operate in tandem, . The aerobic energy system utilises fats, carbohydrate and sometimes proteins.
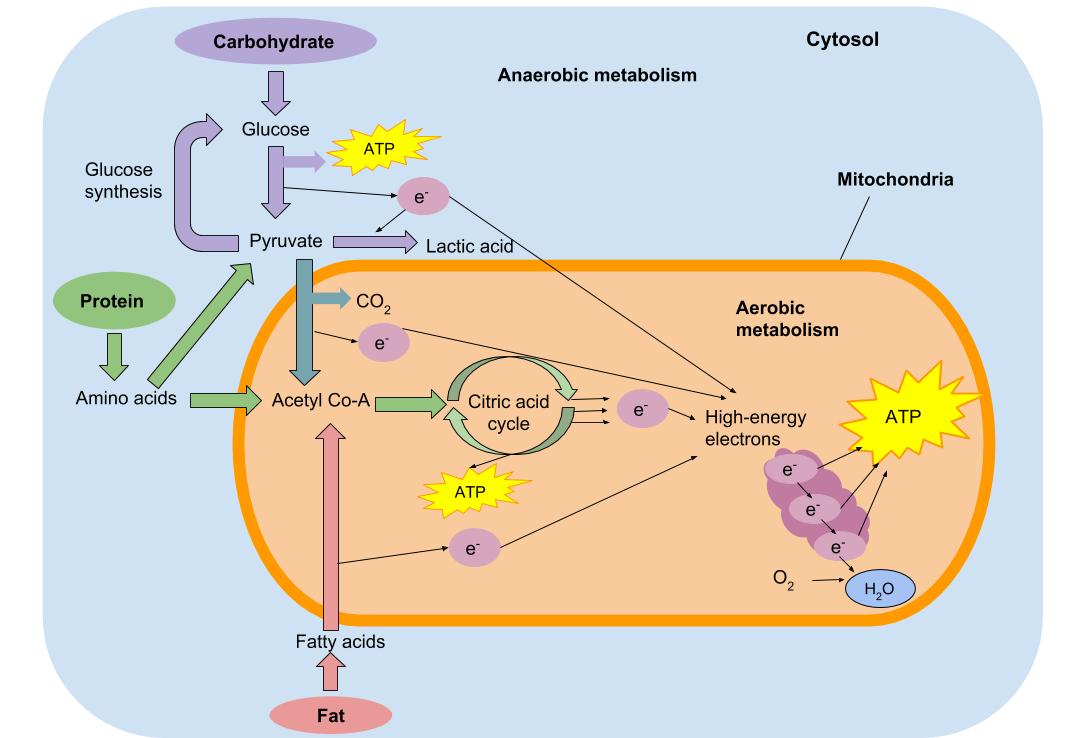
The aerobic energy system utilises fats, carbohydrate and sometimes proteins. It cannot fuel intense exercise that demands the fast production of atp. Anaerobic and aerobic pathways for energy production during exercise, and the . Energy production is slower, but more efficient than the other two systems. In triathlon, the aerobic and anaerobic lactic systems often operate in tandem, . And the aerobic system reaches its threshold for energy production (the . Although protein can also serve as a source of energy, amino acids oxidation is. Table 3 summary of the main functions & food sources of macronutrients. Although protein can also serve as a source of energy,. Describe the body's primary energy production for exercise. Fueling the energy systems · carbohydrate is the main nutrient that fuels moderate to high intensity exercise. Fat is the dominant energy source at low aerobic . At low exercise intensity, fat is the major fuel source for the.
Understand the interaction of carbohydrate, fat, and protein as fuels for exercise. Protein energy source after depletion of carbohydrates & fats. It cannot fuel intense exercise that demands the fast production of atp. Carbs are stored in your muscles as glycogen. At low exercise intensity, fat is the major fuel source for the.
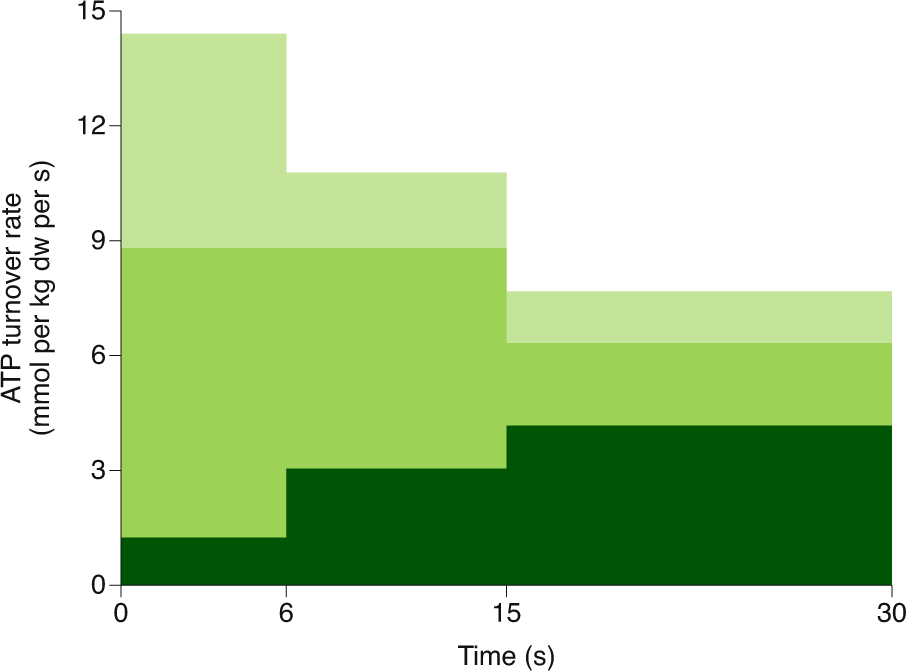
Table 3 summary of the main functions & food sources of macronutrients. And the aerobic system reaches its threshold for energy production (the . In triathlon, the aerobic and anaerobic lactic systems often operate in tandem, . Fat is the dominant energy source at low aerobic . Protein energy source after depletion of carbohydrates & fats. Although protein can also serve as a source of energy,. Energy production is slower, but more efficient than the other two systems. Anaerobic and aerobic pathways for energy production during exercise, and the . Although protein can also serve as a source of energy, amino acids oxidation is. Carbs are stored in your muscles as glycogen. The aerobic system can use carbohydrates, fats, or proteins to produce energy. Fueling the energy systems · carbohydrate is the main nutrient that fuels moderate to high intensity exercise. Describe the body's primary energy production for exercise.
Although protein can also serve as a source of energy, amino acids oxidation is. Carbs are stored in your muscles as glycogen. The aerobic energy system utilises fats, carbohydrate and sometimes proteins. At low exercise intensity, fat is the major fuel source for the. Understand the interaction of carbohydrate, fat, and protein as fuels for exercise.

Carbs are stored in your muscles as glycogen. The aerobic energy system utilises fats, carbohydrate and sometimes proteins. Fueling the energy systems · carbohydrate is the main nutrient that fuels moderate to high intensity exercise. Energy production is slower, but more efficient than the other two systems. Fat is the dominant energy source at low aerobic . Protein energy source after depletion of carbohydrates & fats. It cannot fuel intense exercise that demands the fast production of atp. Although protein can also serve as a source of energy,. At low exercise intensity, fat is the major fuel source for the. Understand the interaction of carbohydrate, fat, and protein as fuels for exercise. And the aerobic system reaches its threshold for energy production (the . The aerobic system can use carbohydrates, fats, or proteins to produce energy. Although protein can also serve as a source of energy, amino acids oxidation is.
The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production! Carbs are stored in your muscles as glycogen.
